Unlocking the Secrets of Programmatic Advertising: A Comprehensive Step-by-Step Overview
Programmatic advertising has revolutionized the way digital advertising operates. This automated and data-driven approach to ad buying and placement has become the industry standard. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the step-by-step process of how programmatic advertising works.
1. Understanding Programmatic Advertising
Programmatic advertising is an automated method for buying and placing digital ads. It uses technology and data to streamline the buying process and make it more efficient. This contrasts with traditional ad buying, which involves manual negotiations and ad placement.
2. Key Components of Programmatic Advertising
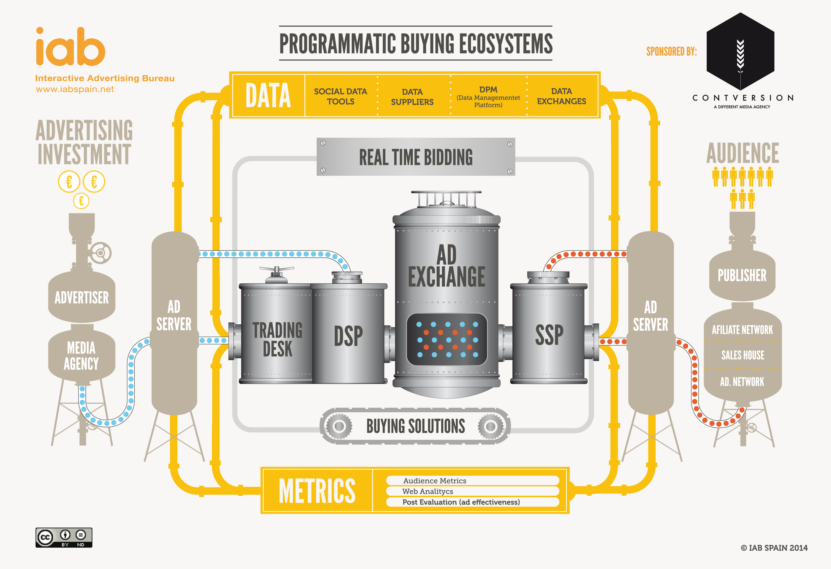
a. Demand-Side Platform (DSP): These platforms allow advertisers to manage their ad campaigns. Advertisers use DSPs to set campaign parameters, budgets, and target audiences.
b. Supply-Side Platform (SSP): Publishers use SSPs to manage their inventory of ad space. SSPs connect publishers with ad exchanges and facilitate the selling of ad impressions.
c. Ad Exchanges: These are online marketplaces where ad space is bought and sold. Ad exchanges are crucial in the programmatic ecosystem because they match advertisers (via DSPs) with publishers (via SSPs) in real-time.
d. Data Management Platforms (DMP): DMPs collect, analyze, and organize data to create a detailed profile of target audiences. This data helps advertisers target their ads more effectively.
3. The Programmatic Advertising Workflow
a. Data Collection and Analysis: Advertisers leverage DMPs to gather and analyze data on user behavior, demographics, and interests. This data is used to create audience segments for targeted advertising.
b. Real-Time Bidding (RTB): When a user visits a website, the ad space is put up for auction on an ad exchange. Advertisers using DSPs bid in real-time to display their ads to specific users based on the audience segments they’ve defined.
c. Ad Placement: The winning bidder’s ad is instantly displayed to the user on the publisher’s website. This entire process occurs within milliseconds, allowing for highly relevant and personalized ad placements.
4. Ad Formats in Programmatic Advertising
Programmatic advertising supports various ad formats, including display ads, video ads, native ads, and mobile ads. Advertisers can choose the format that best suits their campaign goals and the user’s device.
5. Targeting and Audience Segmentation
Programmatic advertising offers precise targeting options. Advertisers can define audience segments based on factors like demographics, location, interests, and online behavior. This level of targeting ensures that ads reach the most relevant audience.
6. Measuring and Optimizing Campaigns
Programmatic advertising provides real-time data on campaign performance. Advertisers can monitor key metrics, such as click-through rates (CTR) and conversions, and make adjustments to optimize their campaigns for better results.
7. Challenges and Concerns in Programmatic Advertising
Programmatic advertising is not without its challenges. Issues such as ad fraud, viewability, and concerns about data privacy and transparency require ongoing attention from the industry.
8. Future Trends and Innovations
Programmatic advertising continues to evolve. Emerging trends include more advanced AI-driven ad targeting, cross-device tracking, and a focus on improving the user experience through less intrusive ad formats.
9. Conclusion
Programmatic advertising is a game-changer in the world of digital advertising. Its data-driven, real-time approach enables advertisers to reach their target audience with precision. Understanding the key components and workflow of programmatic advertising is crucial for advertisers looking to stay ahead in this dynamic and ever-changing landscape. As technology and strategies evolve, the potential for programmatic advertising to deliver effective and engaging campaigns will only continue to grow.
Source – IAB
Programmatic advertising has revolutionized the way digital advertising operates. This automated and data-driven approach to ad buying and placement has become the industry standard. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the step-by-step process of how programmatic advertising works.
1. Understanding Programmatic Advertising
Programmatic advertising is an automated method for buying and placing digital ads. It uses technology and data to streamline the buying process and make it more efficient. This contrasts with traditional ad buying, which involves manual negotiations and ad placement.
2. Key Components of Programmatic Advertising
a. Demand-Side Platform (DSP): These platforms allow advertisers to manage their ad campaigns. Advertisers use DSPs to set campaign parameters, budgets, and target audiences.
b. Supply-Side Platform (SSP): Publishers use SSPs to manage their inventory of ad space. SSPs connect publishers with ad exchanges and facilitate the selling of ad impressions.
c. Ad Exchanges: These are online marketplaces where ad space is bought and sold. Ad exchanges are crucial in the programmatic ecosystem because they match advertisers (via DSPs) with publishers (via SSPs) in real-time.
d. Data Management Platforms (DMP): DMPs collect, analyze, and organize data to create a detailed profile of target audiences. This data helps advertisers target their ads more effectively.
3. The Programmatic Advertising Workflow
a. Data Collection and Analysis: Advertisers leverage DMPs to gather and analyze data on user behavior, demographics, and interests. This data is used to create audience segments for targeted advertising.
b. Real-Time Bidding (RTB): When a user visits a website, the ad space is put up for auction on an ad exchange. Advertisers using DSPs bid in real-time to display their ads to specific users based on the audience segments they’ve defined.
c. Ad Placement: The winning bidder’s ad is instantly displayed to the user on the publisher’s website. This entire process occurs within milliseconds, allowing for highly relevant and personalized ad placements.
4. Ad Formats in Programmatic Advertising
Programmatic advertising supports various ad formats, including display ads, video ads, native ads, and mobile ads. Advertisers can choose the format that best suits their campaign goals and the user’s device.
5. Targeting and Audience Segmentation
Programmatic advertising offers precise targeting options. Advertisers can define audience segments based on factors like demographics, location, interests, and online behavior. This level of targeting ensures that ads reach the most relevant audience.
6. Measuring and Optimizing Campaigns
Programmatic advertising provides real-time data on campaign performance. Advertisers can monitor key metrics, such as click-through rates (CTR) and conversions, and make adjustments to optimize their campaigns for better results.
7. Challenges and Concerns in Programmatic Advertising
Programmatic advertising is not without its challenges. Issues such as ad fraud, viewability, and concerns about data privacy and transparency require ongoing attention from the industry.
8. Future Trends and Innovations
Programmatic advertising continues to evolve. Emerging trends include more advanced AI-driven ad targeting, cross-device tracking, and a focus on improving the user experience through less intrusive ad formats.
9. Conclusion
Programmatic advertising is a game-changer in the world of digital advertising. Its data-driven, real-time approach enables advertisers to reach their target audience with precision. Understanding the key components and workflow of programmatic advertising is crucial for advertisers looking to stay ahead in this dynamic and ever-changing landscape. As technology and strategies evolve, the potential for programmatic advertising to deliver effective and engaging campaigns will only continue to grow.
Source – IAB



